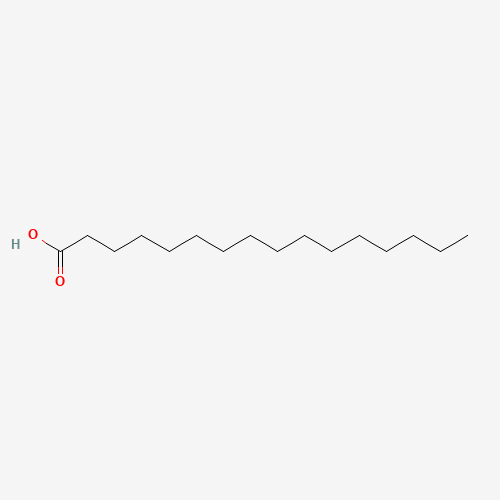
Palmitate
Palmitate is a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C16H32O2. It is the most common fatty acid found in animals, plants, and microorganisms. Palmitate is a major component of the oil from the fruit of oil palms, making up to 44% of total fats.
Palmitate is produced in the body during fatty acid synthesis. It is also obtained from the diet through the consumption of animal and plant products. Palmitate is a major source of energy for the body and is also used to synthesize cell membranes and hormones.
Palmitate can be converted to other fatty acids, such as stearic acid and oleic acid. It can also be converted to triglycerides, which are stored in the body as fat.
Palmitate has a number of important biological functions, including:
- Energy production: Palmitate is a major source of energy for the body. It is broken down in the cells to produce ATP, which is the body's energy currency.
- Cell structure: Palmitate is a major component of cell membranes. It helps to give cell membranes their structure and fluidity.
- Hormone synthesis: Palmitate is used to synthesize a number of hormones, including testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol.
- Signal transduction: Palmitate plays a role in signal transduction, which is the process by which cells communicate with each other.
While palmitate is an essential nutrient, too much palmitate can be harmful to health. High levels of palmitate in the blood have been linked to a number of chronic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
Palmitate is a versatile and important fatty acid with a wide range of biological functions. It is essential for good health, but it is important to consume palmitate in moderation.
Palmitic acid, also known as cetylic acid or hexadecanoic acid, is one of the most common saturated fatty acids found in both animals and plants. Its systematic name, palmitic acid, is often represented by the numbers 16:0 (formula C16:0), indicating its composition of 16 carbons with no ethylenic bond. Its conjugate base, the palmitate ion, forms salts and esters.
Palmitic acid is widely present in the adipose tissues of animals and plays an essential role in various biological processes. It is commonly utilized in the production of soaps, cosmetics, and foods due to its emulsifying and stabilizing properties. As a major component of dietary fats, it contributes to the flavor and texture of many common foods. Additionally, this saturated fatty acid is involved in regulating various metabolic pathways, including lipid biosynthesis and intracellular transport. Its role in cellular function and human physiology overall is of increasing interest in biological and biomedical research.
Accession Number : KLM0000296 This work is released into the public domain; please see our release statement.
Synonyms :
- n-hexadecanoate
Config Rule :
% palmitate
config(palmitate,[
chain([
carboxyl(1),
num(methandiyl,14),
methyl])]).
Smiles String :
[C@2H2]([C](=[O])[O-])[C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][_ C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][C@2H2][CH3] palmitate
Fischer Diagram :

Terminal :
% palmitate
c(1,12,(0,nonchiral))-[o(1,nil)?,c(2,right)~,o(2,nil)?],
c(2,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(1,left)~,c(3,right)~,h(2,up)~,h(1,down)~],
c(3,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(2,left)~,c(4,right)~,h(4,up)~,h(3,down)~],
c(4,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(3,left)~,c(5,right)~,h(6,up)~,h(5,down)~],
c(5,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(4,left)~,c(6,right)~,h(8,up)~,h(7,down)~],
c(6,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(5,left)~,c(7,right)~,h(10,up)~,h(9,down)~],
c(7,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(6,left)~,c(8,right)~,h(12,up)~,h(11,down)~],
c(8,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(7,left)~,c(9,right)~,h(14,up)~,h(13,down)~],
c(9,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(8,left)~,c(10,right)~,h(16,up)~,h(15,down)~],
c(10,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(9,left)~,c(11,right)~,h(18,up)~,h(17,down)~],
c(11,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(10,left)~,c(12,right)~,h(20,up)~,h(19,down)~],
c(12,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(11,left)~,c(13,right)~,h(22,up)~,h(21,down)~],
c(13,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(12,left)~,c(14,right)~,h(24,up)~,h(23,down)~],
c(14,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(13,left)~,c(15,right)~,h(26,up)~,h(25,down)~],
c(15,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(14,left)~,c(16,right)~,h(28,up)~,h(27,down)~],
c(16,12,(0,nonchiral))-[c(15,left)~,h(29,right)~,h(31,up)~,h(30,down)~],
h(1,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(2,up)~],
h(2,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(2,down)~],
h(3,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(3,up)~],
h(4,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(3,down)~],
h(5,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(4,up)~],
h(6,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(4,down)~],
h(7,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(5,up)~],
h(8,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(5,down)~],
h(9,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(6,up)~],
h(10,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(6,down)~],
h(11,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(7,up)~],
h(12,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(7,down)~],
h(13,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(8,up)~],
h(14,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(8,down)~],
h(15,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(9,up)~],
h(16,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(9,down)~],
h(17,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(10,up)~],
h(18,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(10,down)~],
h(19,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(11,up)~],
h(20,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(11,down)~],
h(21,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(12,up)~],
h(22,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(12,down)~],
h(23,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(13,up)~],
h(24,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(13,down)~],
h(25,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(14,up)~],
h(26,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(14,down)~],
h(27,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(15,up)~],
h(28,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(15,down)~],
h(29,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(16,left)~],
h(30,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(16,up)~],
h(31,1,(0,nonchiral))-[c(16,down)~],
o(1,16,(-5.0E-01,nonchiral))-[c(1,nil)?],
o(2,16,(-5.0E-01,nonchiral))-[c(1,nil)?]
The Terminals for all the Config Rules are in Prolog Definite Clause Grammar (DCG) form.They can be checked in the Manual here.
The compound's PDB file can be seen here.